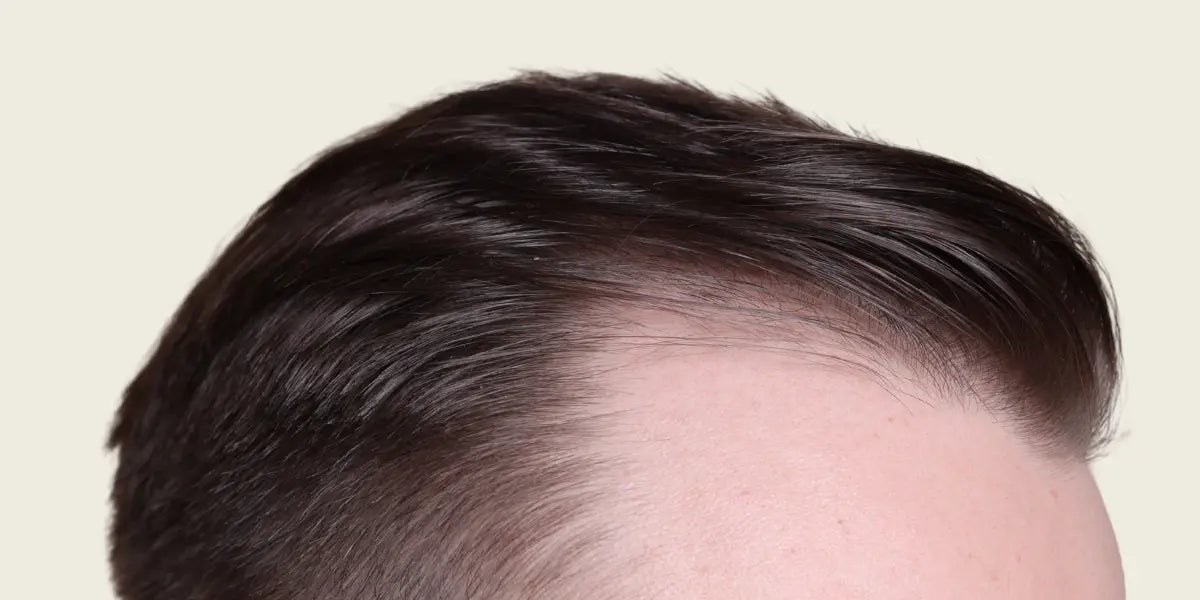
Minoxidil can assist with stopping a hairline from receding. It is not exactly clear how minoxidil works but may have its effect by increasing blood flow to the follicle or by stimulating follicle size and cellular proliferation leading to increased anagen (growth) phase, allowing hair to grow thicker and longer.
Like with finasteride or dutasteride, minoxidil is generally more effective with crown balding than for a receding hairline/temporal recession. (1)


Getting a prescription for minoxidil is easy.
Our intake process takes minutes and every case is reviewed by a licensed doctor.
What Causes a Receding Hairline?
Being genetically predisposed to DHT (dihydrotestosterone) sensitivity is the most common cause of a receding hairline in men and post-menopausal women. A man’s age factors in with receding hairlines normally starting in their late 20s to early 30s. (2) Hormonal fluctuations such as with rapid weight loss eg: as a result of using GLP-1 drugs, (3) certain other medications, a poor diet, certain infections and immune conditions, or high levels of stress can contribute to a receding hair line. But genetics is by far and away the most common and most powerful trigger. (4)
What Is Minoxidil (Rogaine)?
Minoxidil was first developed md approved by the FDA in 1979 to treat elevated blood pressure (hypertension). But it was not long before minoxidil was observed to help improve hair growth for which it got approved in 1988 as an initial 2% topical solution. It was branded by the drug company, Upjohn, as Rogaine. Interestingly, the FDA rejected their first choice of brand name which was Regain. Rogaine is now available over the counter (OTC) in 2% and 5% solutions including a foam form, and is also available off label in an oral form which is accessible by prescription. The topical 5% solution or foam is generally used as it has been shown to have a better clinical effect compared with the 2% solution.
The foam formulation is free of propylene glycol which can be irritant to the skin. So the foam form is often chosen over other solution formulations, as it has a lower risk of skin irritation.
Minoxidil and particularly, the oral form, can have cardiovascular side effects due to systemic absorption (Into the blood stream), and you always must ensure you are being monitored by your doctor when taking oral minoxidil.
Does Minoxidil Work for a Receding Hairline?
Minoxidil works for assisting with stopping a receding hairline and it also has a benefit in causing new hair to grow. It does so by stimulating the anagen (or growth) phase of the hair allowing it to grow longer and thicker and it also increases the size of miniaturized hairs.
The best effects are generally experienced by combining minoxidil with finasteride or dutasteride. This is likely because the combination has maximum impact on the hair follicle including inhibiting DHT in the scalp which is key to the treatment of androgenic alopecia (AGA). (5)
Should You Try Minoxidil on Your Receding Hairline?
It is often advisable to try minoxidil to stop a receding hairline. If you see some results but want to improve them further, ask your doctor about including finasteride or dutasteride as well. Using both medications consistently is your best option for stopping a receding hairline.
What Else Can You Use for a Receding Hairline?
There are multiple options available to use when trying to stop a receding hairline. Finasteride, dutasteride, minoxidil, low level laser hair therapy (6), microneedling (7), and supplements known to help with hair and scalp health such as biotin, zinc, and saw palmetto may all be useful in stopping a receding hairline. (8)
How you respond to each will vary and finding which is right for you is best done with doctor supervision.
Finasteride and Minoxidil Combination Treatment For Receding Hairlines
Minoxidil has been shown to have a good success rate in stopping a receding hairline and is approved for this indication. Adding finasteride raises that success rate further by stopping miniaturization of the hair follicle and promoting growth phase leading to stronger and thicker hair. Using these medications in combination hits hair loss via multiple different mechanisms, which is why it’s so much more effective together. (9)
How to Use Minoxidil for Hairline Regrowth
It’s very easy to use minoxidil on a receding hairline. Starting with a clean and dry scalp, apply 1ml (about a half cap) of solution or foam to the area where you have noticed thinning, and massage in gently for 30 to 60 seconds. Do this twice a day with around 10-12 hours in between dosages.
Using a higher dose than the approved dosages of the 5% will not be more effective so stick to 0.5ml (1/2 a capful) of the foam and 1ml (one full capful) of the solution twice daily. Make sure to wash your hands after each application. Follow up with some pictures so you can track your progress and switch to something else or add finasteride if you find it isn’t working well for you.
How Long Does Minoxidil Take to Work?
Using minoxidil on your hairline will yield results in roughly 4-6 months with peak results seen around 9-12 months and sometimes longer. You can expect hair shedding to occur at around 1-3 months. This is temporary and will resolve.
You’ll notice this is a similar pattern with other hair loss medications such as finasteride and dutasteride. This is because the old follicles first need to shed before the new ones grow in healthier and fuller. The treatments accelerate that shedding by reducing the catagen (where hair growth stops) and telogen (resting) phases which then forces new hairs out.
Side Effects of Minoxidil
Using minoxidil to stop a receding hairline normally has a low risk of side effects. Those that do occur are generally local and include itching on your scalp, flaking and redness. Temporary shedding can happen but generally is limited and does not last more than a few weeks to months. In rare cases, some users have reported dizziness, palpitations or swelling of the ankles or around the eyes. These symptoms are more common with oral minoxidil than topical forms and in these cases, you should stop using the medication and talk to your doctor right away. Remember to never apply minoxidil to your skin if it’s already inflamed or in any way damaged. (10)
Oral vs. Topical Minoxidil
Topical minoxidil is a generally a better tolerated option than oral minoxidil. Because the oral formulation is absorbed into the bloodstream in higher amounts, it means an increased potential risk of side effects. Many users find that it’s best to try the topical option first and if the results aren’t good, then talking to a doctor about getting a prescription for the oral form might be the next best step.
Rogaine vs. Generic Minoxidil
Rogaine is the brand name for topical minoxidil and uses the same active ingredient. The generic variety is more affordable and will have the same effect on stopping your receding hairline as Rogaine.
When Minoxidil Doesn’t Work on a Receding Hairline
If your hairline has already receded to the point that there are no follicles left, then minoxidil won’t help. Using the medication inconsistently or stopping early because you see shedding or haven’t seen results yet will also be ineffective. Make sure you’re applying it onto your scalp and not your hair and if you don’t see any changes after 6-12 months, then talk to a doctor about other treatment option.
How to Repair or Strengthen a Receding Hairline
Using minoxidil with finasteride or dutasteride might be your best option for treating a receding hairline. However, in combination with this, there are lifestyle changes you can make as well. Getting the right amount of protein (11), iron (12), zinc (13), and vitamin D (14) are all natural ingredients considered important for strengthening your hairline. Gentle shampoos (15) that don’t have sulfates or other chemicals (eg parabens), low level light therapy are other adjuncts such as scalp massage (16) to consider, and if you smoke, then now is the time to quit. (17)
How to Stop a Receding Hairline from Getting Worse
The best way to stop your hairline from receding is to start taking action now. If you combine DHT blockers like finasteride or dutasteride with minoxidil as soon as you notice thinning, then you greatly improve your chances of keeping your existing hairline. Use the medications consistently and have patience. Stopping hair loss is a lifelong commitment but if you stay with it and keep treating the problem consistently, then you have a very good chance of keeping your hairline.
Before and After Stopping a Receding Hairline

Before and after using XYON’s topical finasteride with minoxidil for 10 months.
Key Takeaways
- Minoxidil works for most men with early hairline recession.
- It’s not a cure, but a proven regrowth and maintenance tool.
- Consistency, early use, and combination therapy are the secrets to success.
- Start before the hairline is gone, and keep it part of your routine.
FAQ
1. Does Minoxidil work for a receding hairline?
Yes, minoxidil can help slow down and even partially reverse a receding hairline if it’s used early enough.
It works by stimulating dormant follicles and increasing blood flow to the frontal scalp, helping new, thicker hairs replace thinning ones.
However, Minoxidil can’t regrow hair on fully bald areas where follicles are no longer active. The earlier you start, the better your results will be.
2. How should I apply Minoxidil to the hairline?
Start with a dry scalp.
Apply the foam or liquid directly along the hairline and temples, where thinning is most visible.
Gently massage it into your scalp with your fingertips for about a minute.
Apply twice daily — once in the morning and once in the evening.
Don’t exceed two applications a day; it won’t improve results and can cause irritation.
Wash your hands thoroughly after applying.
3. How long does it take to see results on a receding hairline?
Results take time, typically:
3–4 months: Thinning may slow; mild shedding can occur as weak hairs are replaced.
6 months: Noticeable thickening around the frontal hairline.
9–12 months: Visible improvement in coverage and density.
Stopping treatment will cause new growth to shed within a few months, so consistency is key.
4. Can Minoxidil regrow my temples or frontal hairline completely?
Minoxidil can thicken existing hair and stimulate regrowth at the edges, but it won’t restore hair where follicles have completely died.
If your temples are shiny or smooth, results will be limited — but most men still notice better fullness and less visible recession when used consistently.
5. Can I combine Minoxidil with other treatments for better hairline results?
Yes, the best outcomes often come from combining treatments:
Finasteride: Blocks DHT, the hormone responsible for hairline recession.
Microneedling: Enhances absorption and follicle stimulation.
Ketoconazole shampoo: Reduces inflammation and DHT buildup on the scalp.
Studies show that Minoxidil + Finasteride together can improve hairline regrowth for over 9 out of 10 men.

Dr. Simon Pimstone, MD PhD FRCPC
Physician-Scientist; Founder, Director, and Chief Executive Officer
XYON: Founder, Director, and CEO
Education
Doctorate of Medicine (MD) — University of Cape Town, South Africa — 1991
Genetics (PhD) — University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands — 1998
Internal Medicine (Postgraduate Fellowship) — University of British Columbia (UBC), Canada — 2001
Academic & Clinical Appointments
Clinical Assistant Professor, Division of General Internal Medicine — University of British Columbia
Associate Member, Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine — University of British Columbia
Faculty — Providence Health Care Heart and Lung Institute
References:
- Messenger AG, Rundegren J. Minoxidil in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150(2):186-194. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.05785.x. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14996087/
- Chen L, Zhang J, Wang L, Wang H, Chen B. The Efficacy and Safety of Finasteride Combined with Topical Minoxidil for Androgenetic Alopecia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2020;44(3):962-970. Epub 2020 Mar 12. doi:10.1007/s00266-020-01621-5. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32166351/
- Cleveland Clinic. DHT (Dihydrotestosterone): What It Is, Side Effects & Levels. Cleveland Clinic Health Library. Last reviewed December 20, 2022. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/24555-dht-dihydrotestosterone
- Asfour L, Cranwell W, Sinclair R. Male Androgenetic Alopecia. In: Feingold KR, Adler RA, Ahmed SF, et al., editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000–. Last Update: January 25, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278957/
- Mammoser G. Why Ozempic, Wegovy May Cause Hair Loss, Plus Tips to Help Treat It. Healthline. August 8, 2025. https://www.healthline.com/health-news/glp-1-drugs-may-cause-hair-loss-treatment
- Godman H. It’s not too late to save thinning hair. Harvard Health Publishing. January 1, 2023. https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/its-not-too-late-to-save-thinning-hair
- Dhurat R, Saraogi P. Hair evaluation methods: merits and demerits. Int J Trichology. 2009;1(2):108-119. doi:10.4103/0974-7753.58553. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24474647/
- Avci P, Gupta GK, Clark J, Wikonkal N, Hamblin MR. Low-level laser (light) therapy (LLLT) for treatment of hair loss. Lasers Surg Med. 2014;46(2):144-151. Epub 2013 Aug 23. doi:10.1002/lsm.22170. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23970445/
- Faghihi G, Nabavinejad S, Mokhtari F, Fatemi Naeini F, Iraji F. Microneedling in androgenetic alopecia; comparing two different depths of microneedles. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20(4):1241-1247. Epub 2020 Sep 29. doi:10.1111/jocd.13714. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32897622/
- Suchonwanit P, Thammarucha S, Leerunyakul K. Minoxidil and its use in hair disorders: a review. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:2777-2786. Published 2019 Aug 9. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S214907. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6691938
- Guo EL, Katta R. Diet and hair loss: effects of nutrient deficiency and supplement use. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2017. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5315033/
- Trost LB, Bergfeld WF, Calogeras E. The diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency and its potential relationship to hair loss. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54(5):824-844. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.11.1104. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16635664
- Park H, Kim CW, Kim SS, Park CW. Zinc supplementation therapy for patients with telogen effluvium: a preliminary report. Ann Dermatol. 2009;21(2):142-144. doi:10.5021/ad.2009.21.2.142. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2861201/
- Saini K, Mysore V. Role of vitamin D in hair loss: A short review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20(11):3407-3414. Epub 2021 Sep 22. doi:10.1111/jocd.14421. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34553483/
- D’Souza P, Rathi SK. Shampoo and Conditioners: What a Dermatologist Should Know? Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60(3):248-254. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.156355. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4458934/
- Koyama T, Kobayashi K, Hama T, Murakami K, Ogawa R. Standardized scalp massage results in increased hair thickness by inducing stretching forces to dermal papilla cells in vitro. Eplasty. 2016;16:e8. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4740347/
- Trüeb RM. Association between smoking and hair loss: another opportunity for health education against smoking? Dermatology. 2003;206(3):189-191. doi:10.1159/000068894. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12673073/